How to Secure Your Home Network Against Cyber Threats
- Niks

- May 2, 2024
- 3 min read
Updated: Dec 17, 2024
Keeping your home network safe is a must these days. Cyber threats can sneak in if you're careless. This guide shows you how to beef up security. Change those default passwords right away. Enable encryption too. Installing firewalls helps a bunch. These steps shield your data and gadgets from hackers. In our tech-filled world, you'll sleep better knowing your network has strong defenses against cyber crooks. Ready to lock things down? Let's get started.
Screenshots of the router interface are from TP-link BE19000 Triband Wi-fi 7 router. Not all routers have the same interface, and you might not find features from BE19000 in your router.
Securing Home Network
Step 1: Change Default Passwords
Ensure that you change the default passwords for your router, modem, and any other network devices. Use strong, unique passwords containing a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
Step 2: Update Firmware Regularly
Keep your router's firmware up to date by regularly checking for updates from the manufacturer. Firmware updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities.
Step 3: Enable Encryption
Enable WPA2 or WPA3 encryption on your Wi-Fi network to encrypt data transmitted between devices and your router. Avoid using outdated encryption protocols like WEP.
Step 4: Use a Strong Network Name (SSID)
Avoid using default or easily guessable network names. Choose a unique SSID that doesn't reveal personal information or identify you.
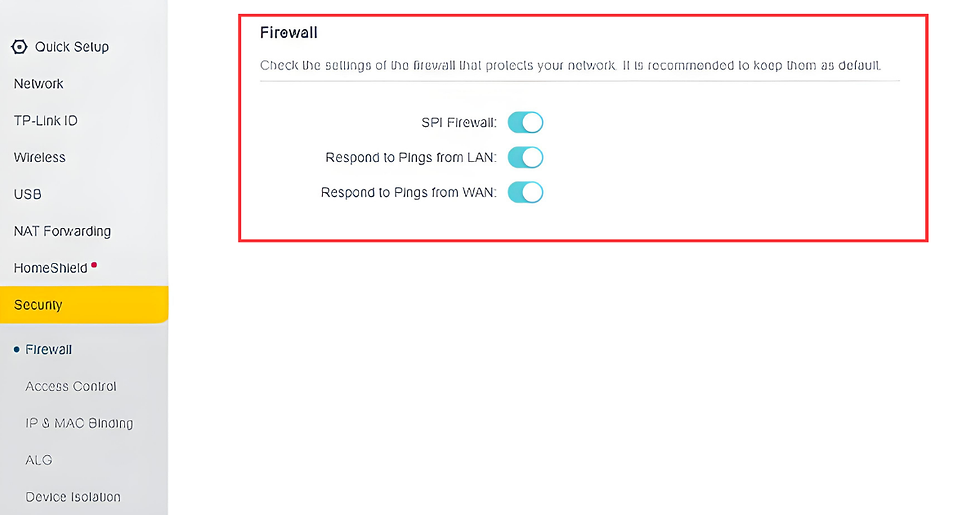
Step 5: Enable Network Firewalls
Most routers come with built-in firewalls. Enable these firewalls to filter incoming and outgoing traffic, providing additional protection against cyber threats.
Step 6: Disable Remote Management
Turn off remote management features on your router if it has that feature. This prevents unauthorized users from accessing and modifying your router's settings remotely.
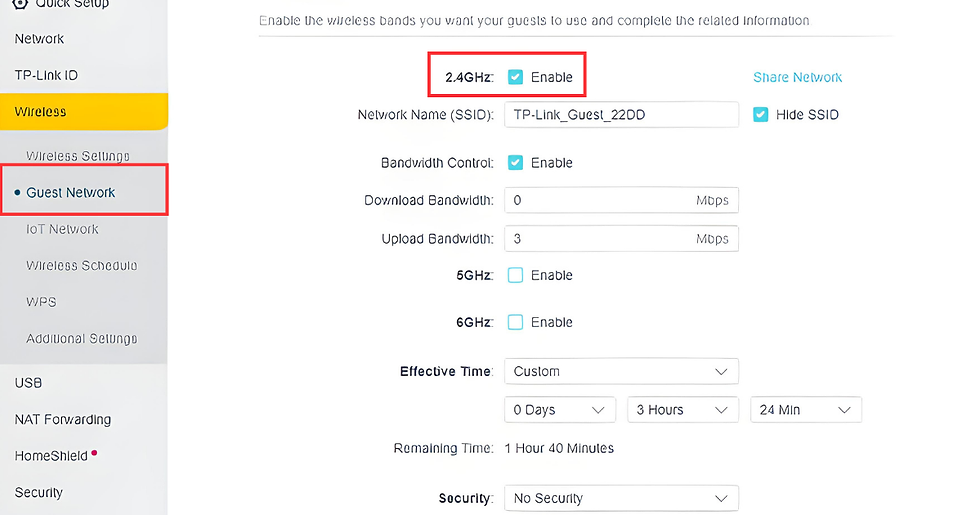
Step 7: Use Guest Networks
If your router supports it, set up a guest network for visitors. This separates guest devices from your primary network, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to your devices and data.
Step 8: Enable MAC Address Filtering
MAC address filtering lets you specify which devices can connect to your network based on their unique MAC addresses. While not foolproof, it adds an extra layer of security.
Step 9: Install Antivirus and Antimalware Software
Install reputable antivirus and antimalware software on all devices connected to your network, including computers, smartphones, and tablets. Keep these programs updated regularly.
Step 10: Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Wherever possible, enable two-factor authentication for accounts associated with your home network devices, such as your router's administrative interface.
Step 11: Regularly Monitor Network Activity
Keep an eye on your network for any unusual or suspicious activity. Many routers offer logging capabilities that allow you to review which devices are connected and what they're doing. Some routers have network-checking features, as shown in the screenshot below.
Step 12: Educate Yourself and Your Family
Educate yourself and your family members about common cyber threats, such as phishing scams and malware, and teach them how to recognize and avoid them.
Conclusion
In conclusion, securing your home network from cyber threats is critical in the digitally interconnected environment. Following the above-provided security steps, you will significantly increase the security of your network, which includes protecting your digital property, personal information, and privacy. Additionally, ensure your devices and software are regularly updated, use strong passwords and encryption processes, and install firewalls and IDS/IPS. Finally, do not ignore any suspicious activity, and ensure you are informed about prospective threats so that you can use the internet without any concerns.